Mother Earth:
The Mother Earth is the third planet from the sun and it is the fifth largest planet in the solar system. It is mentioned as the blue planet due to the appearance of blue colored sphere when looked up from the space. Earth is said to be formed about 4.54 billion years ago and the life in earth has originated within one billion years. The Mother Earth is the home of millions of specious including the valuable human beings.

Uniqueness of Earth compared to other planets:
- Earth is a terrestrial planet which means it the place where inhabitation of various living beings while the other planets cant.
- Orbit: 149,600,000 km (1.00 astronomical unit) from sun
- Diameter: 12,756.3 km
- Mass: 5.972e(24) kg
Earth is divided into several layers with variation in physical, chemical and seismic(underground movement, vibration at the interior of the Earth) properties.
The inner core of the earth is mainly composed of iron with nickel and some traces of other lighter elements may also present. The lower mantle consists of metals silicon and magnesium and oxygen with some iron, calcium and aluminium. The upper mantle has olivene and pyroxene (iron/magnesium silicates) with some calcium and aluminium. The crust is primarily composed of quartz (silicon-di-oxide) and other silicates like feldspar.
The total chemical composition of Earth by mass is
What is Pillow Lava?
A pillow lava is a lava erupted under water. They don't always have the classic "tear drop" shape, but they can be spherical or tube like.
The low eruption rate means that the lava can obtain and retain the shapes. The shape occurs when the hot lava erupting, comes in contact with the cool water. The outer most lava cools very rapidly and forms a glassy "skin", and lava keeps filling the inside of the skin, till it breaks away. The inside of the pillow crystallises much slower than the outside so the grains are coarser. Pillow Lavas occur wherever there is mafic to intermediate grade lava erupting in a sub-aqueous environment. Such locations can include, but are not limited to hot spots and mid oceanic ridges.
Pillow Lavas can be used to determine way-up structures in the geological record using 3 criteria (these criteria are not always accurate and in some cases a pillow that appears to be the right way up has been altered and the last two criteria only relate to the classic "pillow shape")

1- Vesicles in the lava will congregate towards the top of the pillow
2- Pillows will generally show a convex upper surface
3- Pillows will hvae a base that tappers downwards.
The oldest pillow lava's have been found in Archean Green stone Belts.
Amazing Rainbow effect
Pillow Lavas can be used to determine way-up structures in the geological record using 3 criteria (these criteria are not always accurate and in some cases a pillow that appears to be the right way up has been altered and the last two criteria only relate to the classic "pillow shape")

1- Vesicles in the lava will congregate towards the top of the pillow
2- Pillows will generally show a convex upper surface
3- Pillows will hvae a base that tappers downwards.
The oldest pillow lava's have been found in Archean Green stone Belts.
Amazing Rainbow effect

The stunning image below is of a rainbow cloud, captured above Mt Everest by Oleg Bartunov whilst on an expedition in the Himalayas, Nepal.The amazing rainbow effect is created when tiny ice crystals in the water vapour of the clouds reflect the sunlight.
ASPERATUS CLOUD FORMATION, NEW ZEALAND
Asperatus (aka undulatus asperatus) cloud formations are very rare worldwide – so rare they were not proposed as a separate cloud classification until 2009. The name translates as roughened or agitated waves. It is thought that asperatus clouds’ choppy undersides may be due to strong winds disturbing previously stable layers of warm and cold air.
Graeme Anderson, an MSc student at the Department of Meteorology, Reading University, studied weather records and used a computer model to simulate the cloud formation. In doing so, Graeme found that asperatus clouds form in the sort of conditions that produce mamma clouds (also known as mammatus); asperatus clouds form when the winds up at the cloud level cause the cloud to shear into wave-like forms known as undulatus.If accepted as a new classification, asperatus will be the first new classification in the World Meteorological Organization's International Cloud Atlas since cirrus intortus in 1951.
This image, captured by Merrick Davies, is of a rather turbulent sky over Hanmer Springs, South Island, New Zealand. Such cloud formations have been seen all over Britain, as well as in the plains of the USA.

Graeme Anderson, an MSc student at the Department of Meteorology, Reading University, studied weather records and used a computer model to simulate the cloud formation. In doing so, Graeme found that asperatus clouds form in the sort of conditions that produce mamma clouds (also known as mammatus); asperatus clouds form when the winds up at the cloud level cause the cloud to shear into wave-like forms known as undulatus.If accepted as a new classification, asperatus will be the first new classification in the World Meteorological Organization's International Cloud Atlas since cirrus intortus in 1951.
This image, captured by Merrick Davies, is of a rather turbulent sky over Hanmer Springs, South Island, New Zealand. Such cloud formations have been seen all over Britain, as well as in the plains of the USA.

PLITVICE LAKES, CROATIA
The Plitvice Lakes National Park is found in the mountainous region of Lika, between Zagreb and Zadar. The lake is surrounded by three mountains; Dinaric Alps, Plejesvica Mountain and Mala Kapela Mountain. 16 lakes are separated by the mountains into upper and lower clusters and the lakes are interconnected by a series of waterfalls. The lakes range in colour from azure to green, blue or grey. They formed from the erosion of chalk sedimentation, forming a karst landscape.
There is an altitude difference between the mountains; the highest point is at 1,280m and the lowest at 380m. The total height difference between the lakes is 135m; Veliki Slap, the largest waterfall, is 70m tall.
The Park was founded in 1949 and was granted UNESCO World Heritage status in 1979. It covers a total area of 300 square kilometres; the lakes join together over a distance of 8 km. It is the oldest national park in Southeast Europe.

Red Beach
This is the aptly named “Red Beach”, located southwest of Panjin City in China’s Liaoning Province. The red colour is attributed to a genus of plant known as Suaeda, also known as Seablite. Suaeda flourishes in the saline-alkali soil at the mouth of the Liaohe River.
The plants appear every year around April or early May, they are originally green in colour. As the plant begins to die it becomes reddish and by September, Suaeda is a brilliant red, covering nearly the entirety of the beach.

This is the aptly named “Red Beach”, located southwest of Panjin City in China’s Liaoning Province. The red colour is attributed to a genus of plant known as Suaeda, also known as Seablite. Suaeda flourishes in the saline-alkali soil at the mouth of the Liaohe River.
The plants appear every year around April or early May, they are originally green in colour. As the plant begins to die it becomes reddish and by September, Suaeda is a brilliant red, covering nearly the entirety of the beach.

Bermuda Triangle
Bermuda Triangle is one of the most popular mystries of the world. Its right to say it as devil's triangle which is situated in the western part of North Atlantic Ocean. The place carries several unexplained questions and cases about missing of aircraft and ships.
The first person who documented about bermuda triangle is Gian J Quasar. His research accomplished about 20 years and he filed large private repository of reports and official documents containing 350 cases over centuries. Of them most were dissapearance cases that has last only 25 years.
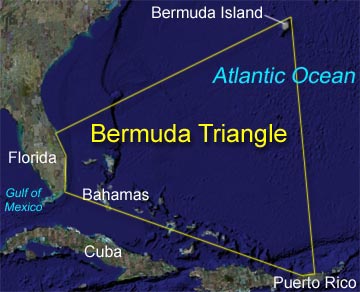
Boundaries of Bermuda Triangle
Bermuda Triangle is one of the most popular mystries of the world. Its right to say it as devil's triangle which is situated in the western part of North Atlantic Ocean. The place carries several unexplained questions and cases about missing of aircraft and ships.

The first person who documented about bermuda triangle is Gian J Quasar. His research accomplished about 20 years and he filed large private repository of reports and official documents containing 350 cases over centuries. Of them most were dissapearance cases that has last only 25 years.
Boundaries of Bermuda Triangle
The boundaries of bermuda triangle covers the Straits of Florida, the Bahamas and the Atlantic east to the Azores. And the most accidents were found concentrated in the Bahamas and the Florida Straits. The area is one of the most intemperatively travelled shipping lanes in the world, essentaily the ships crossing for their ports in America, Europe and Caribbean Islands. It is also a heavily travelled air route towards Florida, Caribbean and South America.
Mammoth Cave, Kentucky, USA
Mammoth Cave in Mammoth National Park is part of the longest cave system in the world, and is a world heritage site.The caves have formed in thick deposits of carboniferous limestone, with a sandstone cap-rock. With over 630 km of passageways and cave, the National Park was established to help preserve and protect the cave system. New discoveries are adding distance to the cave system every year. The Geology of the caves has been put together really well in the documentary "Geology of Mammoth Cave, Kentucky", by University Students at Ohio State.
The Siberian branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences has revealed that the 100 kilometre wide Popigai Astroblem crater, from a meteorite which hit Earth 35 million years ago, contains a dense deposit of industrial diamonds (good for technological purposes but not jewelry). The deposit was apparently discovered in the 1970’s, but the Soviets decided to keep it a secret so that they didn’t upset a world diamond market that already favoured them. Nikolai Pokhilenko, the head of the Geological and Mineralogical Institute in Novosibirsk, has said that the diamonds include other molecular forms of carbon, and that they could be twice as hard as conventional diamonds. He said the Popigai diamonds could revolutionise the global market in industrial diamonds.
There are two main explanations for the formation of ‘impact diamonds’, found in small quantities at meteorite-impact sites around the Earth. If a meteor slams into an area rich with carbon, like the remains of living organisms, then the high pressures and temperatures of the collision would be enough to turn the terrestrial carbon into diamond. Another possibility is that the carbon arrives on Earth inside the meteorite, and is then flash-fused into diamonds on impact. There have been discoveries of meteorites embedded with tiny diamonds, but neither of the scenarios posited is known to create the amount of diamonds that Russia claims has been discovered.













1 comments:
Hello Mr.Jenish,
It looks so good and very informative....Hats off for ur great effort in creating these stuff...I like to have more stuff...will be visiting often....:) :)
Post a Comment